This is the Trumpeter 00406 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Leopold Gun crew’.

History
Manufacturer
Where I got it
- Hobbymesse 2017
This is the Trumpeter 00406 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Leopold Gun crew’.

This is the ICM 35451 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Truck, KHD S3000’.

The first prototypes of the new Magirus 3 ton lorry made in 1939 were labeled Magirus S/A 330. The vehicles of the serial production started in 1940 had the name Klöckner-Deutz S/A 330. Beginning in 1941, it was changed to S/A 3000.
The Klöckner-Deutz S/A 3000 was powered by a 4 cylinder, 80 HP Deutz diesel engine. The Klöckner-Deutz S3000 lorries, with a standard box body’s were used by the Luftwaffe.
Special vehicles like fire fighting vehicle were made on the chassis of the Klöckner-Deutz S3000.
This is the ICM 35466 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Truck, Henschel 33 D1’.

In the course of the first program for motorising the Reichswehr from 1926, development of three-axled cross-country lorries with a payload of 3 tons was demanded besides others.
Three companies were involved in the development: Büssing, Henschel and Krupp. The first Henschel model – the Henschel type 33 B1 – was delivered in 1928. The vehicles delivered to the Reichswehr had spoke rims with three spokes and dual tyres on the rear axles. In 1929, the Henschel type 33 D1 with the stronger D engine entered serial production.
Compared to the Henschel type 33 B1, the Henschel type 33 D1 had a longer engine bonnet.
This is the ICM 35413 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Truck, Ford G917T – 1939 production’.

The Ford 3 tons lorry model 1939 was made with the open standard driver’s cab of the Wehrmacht. Altogether, about 25,000 Ford 3 tons lorries model 1939 were manufactured.
The (Wehrmacht models in braces) G917T (G917T St IIIa) had a 3.6l engine and the G997T (G997T St IIIb) had a 3.9l engine.
This is the Trumpeter 01520 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German 3.7cm FlaK 43 Flakpanzer IV – Ostwind’.

Like the “Wirbelwind” the “Ostwind” had a distinctive angular turret, this time six sided, and with the gun emerging from a slot in the pointed front of the turret.
After trials in July, on 18 August 1944 Ostbau were given a contract to produce 100 “Ostwind”. Less than half of these vehicles would be produced – the first fifteen of the eventual total of forty-three were completed in December 1944, far too late to have any impact on the war.
This is the HobbyBoss 80130 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Pz.Kpfw.IV Ausf. C’.

Designed as an infantry-support tank, the Panzer IV was not originally intended to engage enemy armor — that function was performed by the lighter Panzer III. However, with the flaws of pre-war doctrine becoming apparent and in the face of Soviet T-34 tanks, the Panzer IV soon assumed the tank-fighting role of its increasingly obsolete cousin.
The most widely manufactured and deployed German tank of the Second World War, the Panzer IV was used as the base for many other fighting vehicles, including the Sturmgeschütz IV assault gun, Jagdpanzer IV tank destroyer, the Wirbelwind self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon, and the Brummbär self-propelled gun.
This is the HobbyBoss 80131 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Pz.Kpfw.IV Ausf. B’.

Designed as an infantry-support tank, the Panzer IV was not originally intended to engage enemy armor — that function was performed by the lighter Panzer III. However, with the flaws of pre-war doctrine becoming apparent and in the face of Soviet T-34 tanks, the Panzer IV soon assumed the tank-fighting role of its increasingly obsolete cousin.
The most widely manufactured and deployed German tank of the Second World War, the Panzer IV was used as the base for many other fighting vehicles, including the Sturmgeschütz IV assault gun, Jagdpanzer IV tank destroyer, the Wirbelwind self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon, and the Brummbär self-propelled gun.
This is the Takom 2023 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German 12.8cm FlaK 40 Twilling’.
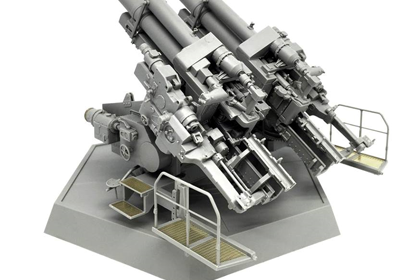
Development of the gun began in 1936, with the contract being awarded to Rheinmetall Borsig, the first prototype gun was delivered for testing in late 1937 and completed testing successfully. The gun weighed nearly 12 tonnes in its firing position, with the result that its barrel had to be removed for transport. Limited service testing showed this was impractical, so in 1938 other solutions were considered.
The eventual solution was to simplify the firing platform, based on the assumption it would always be securely bolted into concrete. The total weight of the system reached 26.5 tonnes, making it practically impossible to tow cross-country. In the end this mattered little, since by the time the gun entered production in 1942, it was used in primary static defensive applications. There were four twin mounts on the fortified anti-aircraft Zoo Tower, and they were also on other flak towers protecting Berlin, Hamburg, and Vienna. Approximately 200 were mounted on railcars, providing limited mobility.
This is the Bronco 35114 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German 88mm FlaK 41 Anti-Aircraft Gun w/Sd.Ah.202 Trailer’.

With the increase of aircraft performance, many armies developed dedicated anti-aircraft guns with a high muzzle velocity – allowing the projectiles to reach greater altitudes. It was this muzzle velocity, combined with a projectile of high weight, that made the 8.8 cm (88mm or “acht-acht”) FlaK one of the great World War II anti-tank guns.
The first such German gun was introduced in 1917, and it used the 88mm caliber, common in the Kaiserliche Marine German navy.
This is the Tamiya 35 237-3900 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Möbelwagen 3,7cm FlaK auf Fgst Pz.Kpfw.IV (Sf)’.

The mass-production model started to be manufactured in February 1944. It was equipped with a powerful 3.7 FlaK 43 cannon capable of firing 250 shots/min, and thick armored plates surrounding the upper part of the vehicle, which could be raised or lowered for horizontal firing.
By 1945, a total of 240 vehicles were produced, most of which were deployed to the western front, providing a vicious defense against approaching fighters and bombers of the Allies.
This is the MiniArt 35162 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Pz.Kpfw.III Ausf. C’.

The Ausf. C still had eight road wheels on each side, with the first and last pairs on a short leaf spring, mounted parallel to the ground. The second and third pairs were supported by a longer leaf-spring assembly. Also featured were a servo-operated epicyclic clutch, brake steering and a new design for the drive sprocket and idler.
By 20 January 1938 there were only twenty-three Pz.Kpfw.III in the total Army Inventory. But this number had increased to forty-two by the end of March 1938. The Ausf. C saw action only in Poland. It was withdrawn from Panzer regiments in February 1940, before the start of the campaign in the West.
This is the Bronco 35174 kit in 1/35 scale, of the ‘German Versuchsflakwagen fur 8.8cm FlaK 37 auf Sonderfahrgestell’.

The Versuchsflakwagen fur 8.8cm – FlaK 41 – was also known as the Grille 10 named after the Cricket insect. The Grille 10 was the first in a series of armoured self propelled guns dating from 1942.
The hull used components from several vehicles but mainly the Panzer IV and Sd.Kfz.9. The gun was mounted on the rear hull and protected by hinged side armour which folded down when in action.
Three prototypes were built in 1944, first mounting the 8.8cm FlaK 37 and later the FlaK 41. One vehicle was refitted with the FlaK 37 and sent to Italy for combat trials, serving with Flakartillerie Abt (Sf) 304 attached to the 26th Panzer Division. Trials were considered a success and a second series of Grille 10’s were ordered, but on Panther hull.
Other members of the Grille family were built on the Tiger II hull including the Grille 17 with 17cm gun, Grille 21 with 21cm mortar, Grille 30 with 30.5cm mortar and the Grille 42 with 42cm mortar.